Outputs¶
After a simulation run SEDobs creates multiple outputs with different formats. Assuming the name of your project is my_simulation_run and the working directory is ~/project/path/ (cf Configuration to find where to give them). SEDobs will create:
Template library¶
~/project/path/my_simulation_run.hdf5: This is the aglomerate of all the galaxy templates SEDobs can choose from to create your simulation. Each simulation comes from this set of templates. They are defined in the ‘Template’ section of the configuration file.
Final simulated catalogs¶
~/project/path/my_simulation_run_photo_file_final.txt [Only if photometry is used]: This is the final photometric catalog produced by SEDobs. It contains all the simulated galaxy with their redshift and their magnitude. The format of this file is the following [we give here the header]:
# ident redshift u-megacam u-megacam_err g-megacam g-megacam_err r-megacam r-megacam_err i-megacam i-megacam_err z-megacam z-megacam_err
The first column gives the name (ident) of the object, the second gives the redshift. Then each magnitude and their error are given. For each measurement in a given filter, two columns are written: The actual measurement (filter_name) and the error on this measurement (filter_name_err). This catalog can be used in the SPARTAN program.
~/project/path/my_simulation_run_spectro_file_final.txt [Only if the spectroscopy is used]: This is the final spectral catalog. It contains all the simulated spectra of the simulated galaxies with their redshift. The format is the following [header for 2-spectra simulation]:
# ident redshift spec1 i-megacam i-megacam_err spec2 J-wircam J-wircam_err
The first column gives again the name (ident) of the object and the second column give the redshift. Then the information for each spectrum is given. For each of them, 3 columns are given: The name of the spectrum (e.g spec1 or spec2) and the normalisation magnitude of this spectrum with its error. In this example i-megacam and i-megacam_err for the first spectrum and J-wircam with J-wircam_err for the second spectrum. This catalog can be used in SPARTAN.
~/project/path/my_simulation_run_Combined_file_final.txt [Only if both spectroscopy and photometry are used]. This is the agglomerate of the two previously presented catalogs. It contains all the photometric and spectroscopic information for each simulated galaxy. An example of a header with 2-spectra and photometric simulation:
# ident redshift spec1 i-megacam i-megacam_err spec2 J-wircam J-wircam_err u-megacam u-megacam_err g-megacam g-megacam_err r-megacam r-megacam_err i-megacam i-megacam_err z-megacam z-megacam_err
The combined catalog start with the same two columns as the other catalogs: ident and redshift. Then the Nx3 next columns are reserved for spectroscopy, with N=number of spectra created during the simulation (see previous point with spectral catalogs). This gives the columns 3 to 8. After the spectroscopic part, All the photometric bands are given; in this example from u to z. For each photometric point the measurement and error are given. In this example this gives columns from 9 to 18 (5 bands times 2).
~/project/path/my_simulation_run_sky_catalog.txt . This catalog will tell you what airmass was considered for each object. If you did not use any sky emission it will be filled by -99.9. If you used the sky emission it will give you the magnitude of the sky (in the normalisation band you defined in the configuration file) and the flux (in erg/s/cm2/Ang) as well as the airmass.
# ident mag_sky flux_sky AMrange1 AM1 AMrange2 AM2….
Individual spectral and photometric files¶
Three directories are created:
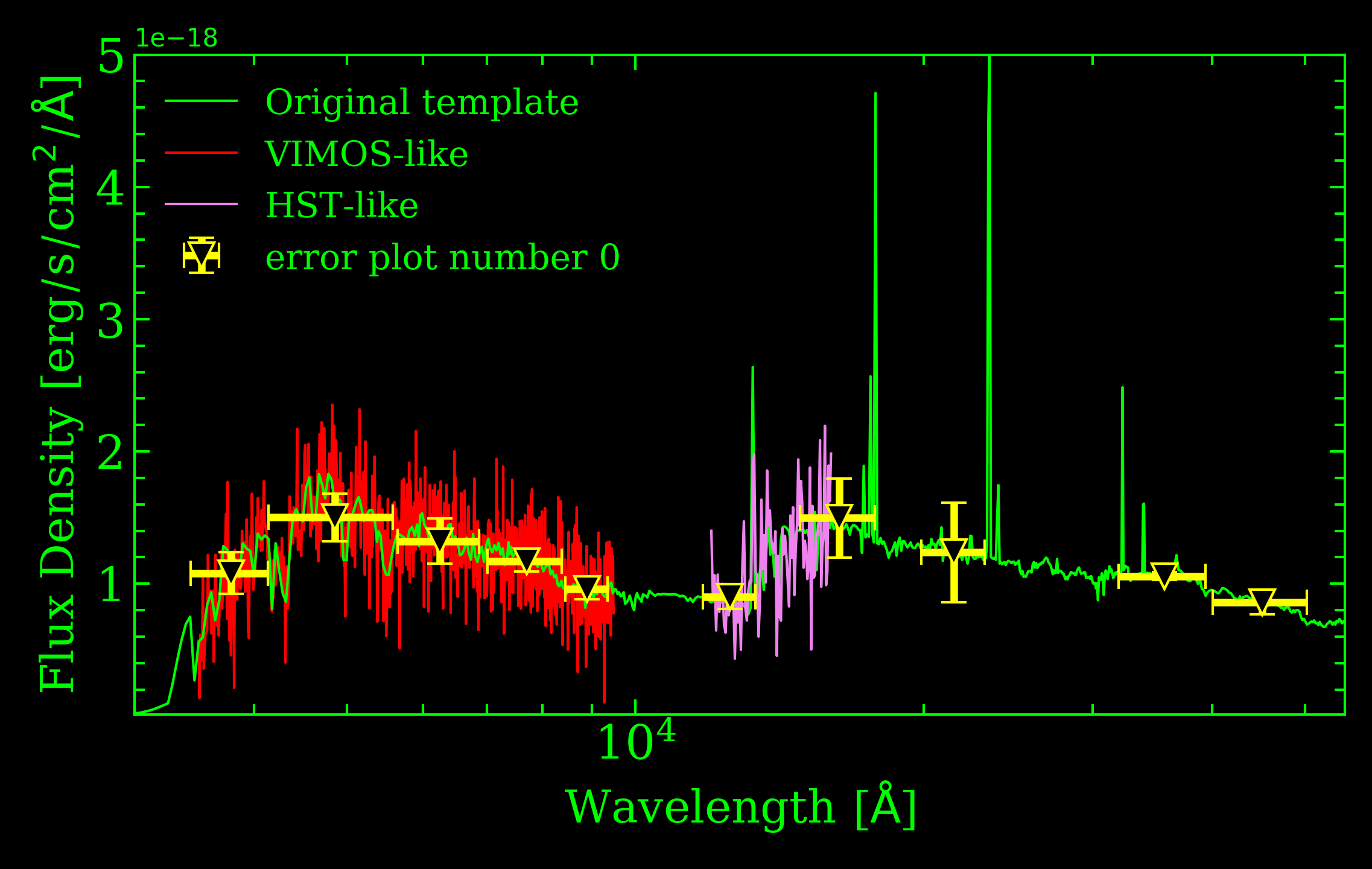
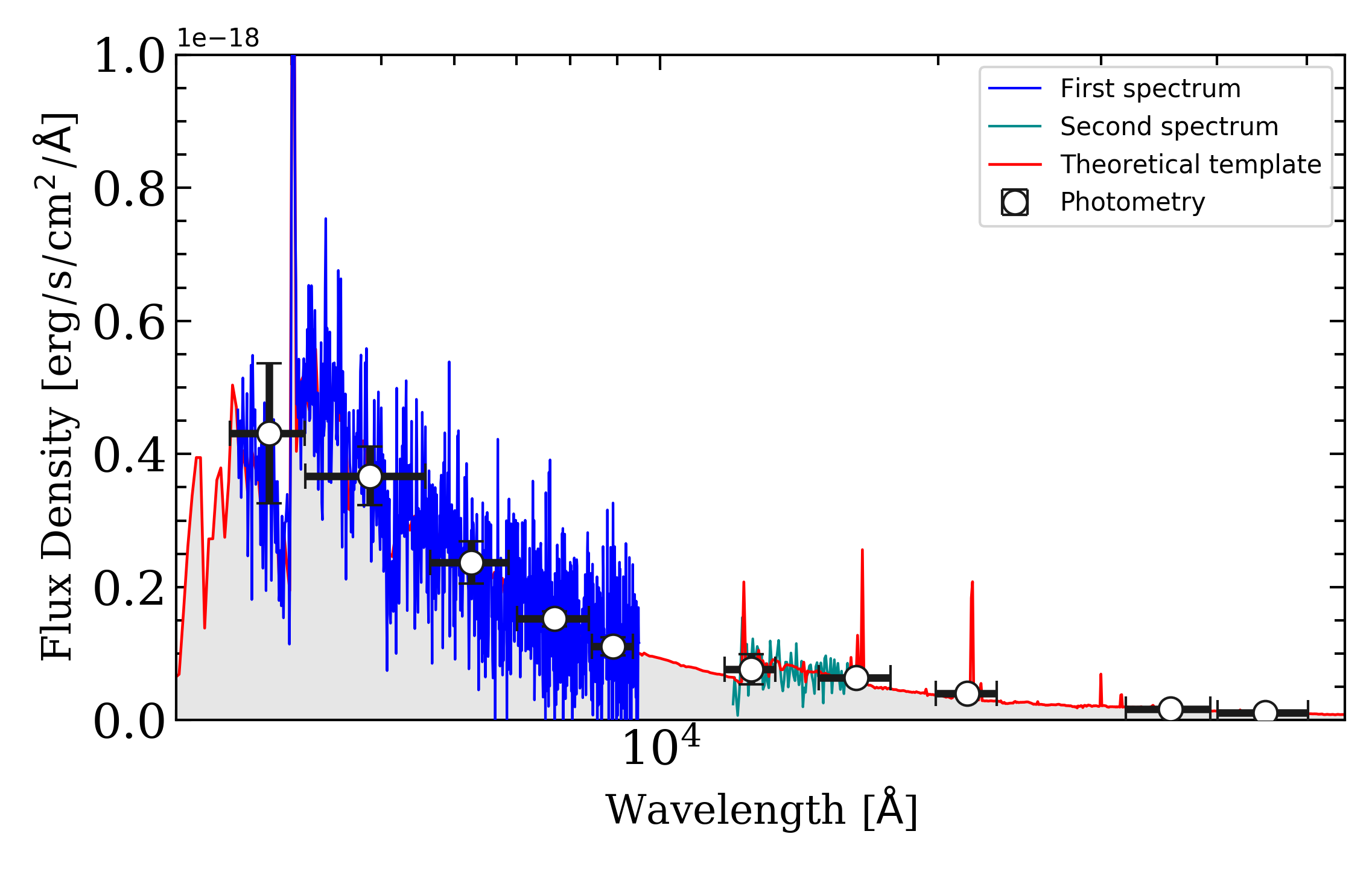
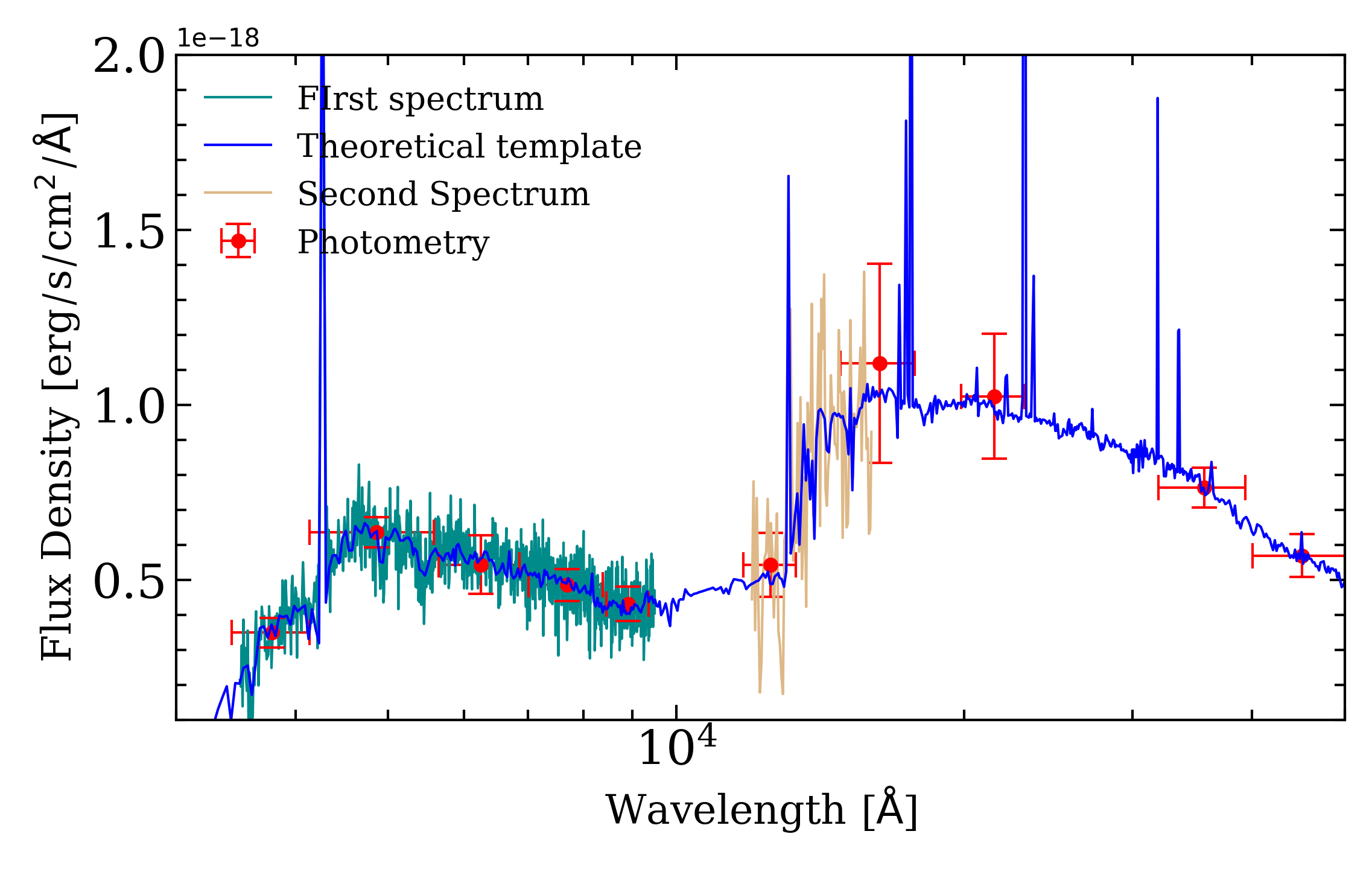
~/project/path/original_template/*: This is the directory where all the template that are actually used are stored. For the first simulated galaxy of the run, the file ~/project/path/original_template/my_simulation_run_N1_original.txt is the theoretical template that was used for the simulation. It is worth noting that it is correctly flux-calibrated. These files contain 2 columns: wavelength (in angstrom) and flux density.
~/project/path/photo_indiv/*: This directory contains all the photometric information for each simulated galaxy. For example, the first simulated galaxy of the run (with photometry of course) will give the file ~/project/path/photo_indiv/my_simulation_run_N1.dat_phot.txt. This files contains all the photometric measurement made for this simulation:
#wavelength wavelength_err mag_template, mag_template_flux, magfinal, error_mag, fluxfinal, errorflux, magsky, Fluxsky
The wavelength is the effective wavelength of each of the band. Wavelength_err give the half the width at half maximum of the filter. Mag_template and Mag_template_flux give the magniude (in AB system) and the flux of the theoretical template used for the simulation with sky applied. Magfinal, errormag, fluxfinal and errorflux gives the final magnitude anf flux (with offset applied) for the simulated galaxy. Finally, the magnitude and flux of the sky are given by magsky and fluxsky.
~/project/path/spectra/*: This directory contains all the spectra of the simulated galaxies. Assuming you asked for two spectra in the configuration of the simulation run the first simulated galaxy will give 2 spectra: ~/project/path/spectra/my_simulation_run_N1_1.txt and ~/project/path/spectra/my_simulation_run_N1_2.txt. Each file contain a spectrum simulated for the first object of the run. The format of these files is: wavelength, flux density and error. Additionnally, the sky spectrum is given for each science spectrum in a different file: ~/project/path/spectra/my_simulation_run_sky_N1_1.txt and ~/project/path/spectra/my_simulation_run_sky_N2_1.txt
Few example of simulated data are shown below:
Note
All the plots have been made using the photon program: http://photon-plot.readthedocs.io/en/latest/index.html